Tools
Here you will find the computational tools developed on the Dalmolin Systems Biology Group. We are committed to the best practices on software developing and documentation. However if you need any help on the usage, feel free to contact us.
Featured
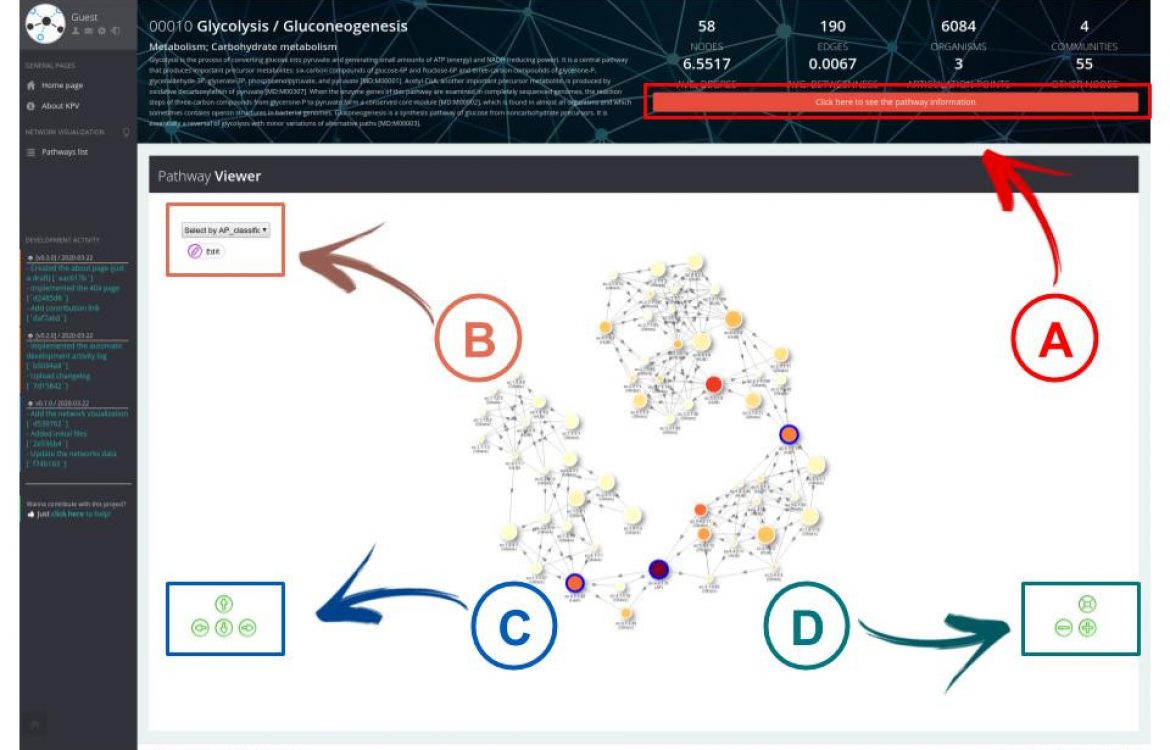
The network elaborated in our study contemplates protein classifications according to the AP detection algorithm,facilitating the visual identification of the most important proteins of a network.
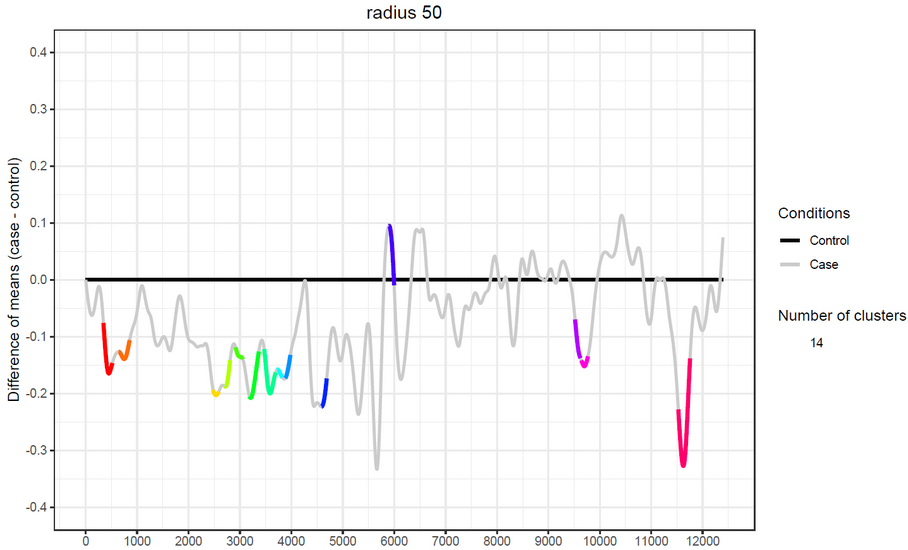
Transcriptograms are genome wide gene expression profiles that provide a global view for the cellular metabolism, while indicating gene sets whose expressions are altered.
More

Geneplast is designed for evolutionary and plasticity analysis based on orthologous groups distribution in a given species tree.
A pipeline for sensitive taxonomic classification and flexible functional annotation of shotgun metagenomic data.

Dalmolin Group’s workflow for pre-processing, alignment and quantification of bulk RNA-seq data.
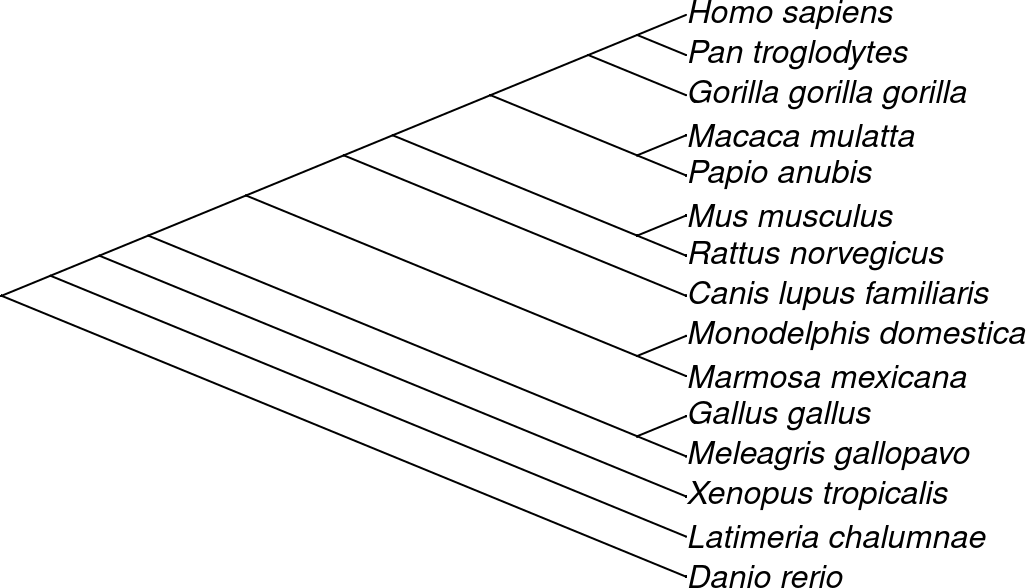
Provides datasets from different sources via AnnotationHub to use in geneplast pipelines. The datasets have species, phylogenetic trees, and orthology relationships among eukaryotes from different orthologs databases.

A Python tool that annotates each query from a BLAST/DIAMOND tabular output using the best alignment for which a mapping is known.

Solves the Seriation problem finding a suitable linear order for a set of proteins. The result is a list of proteins ordered in one dimension such that functionally associated proteins are closer.